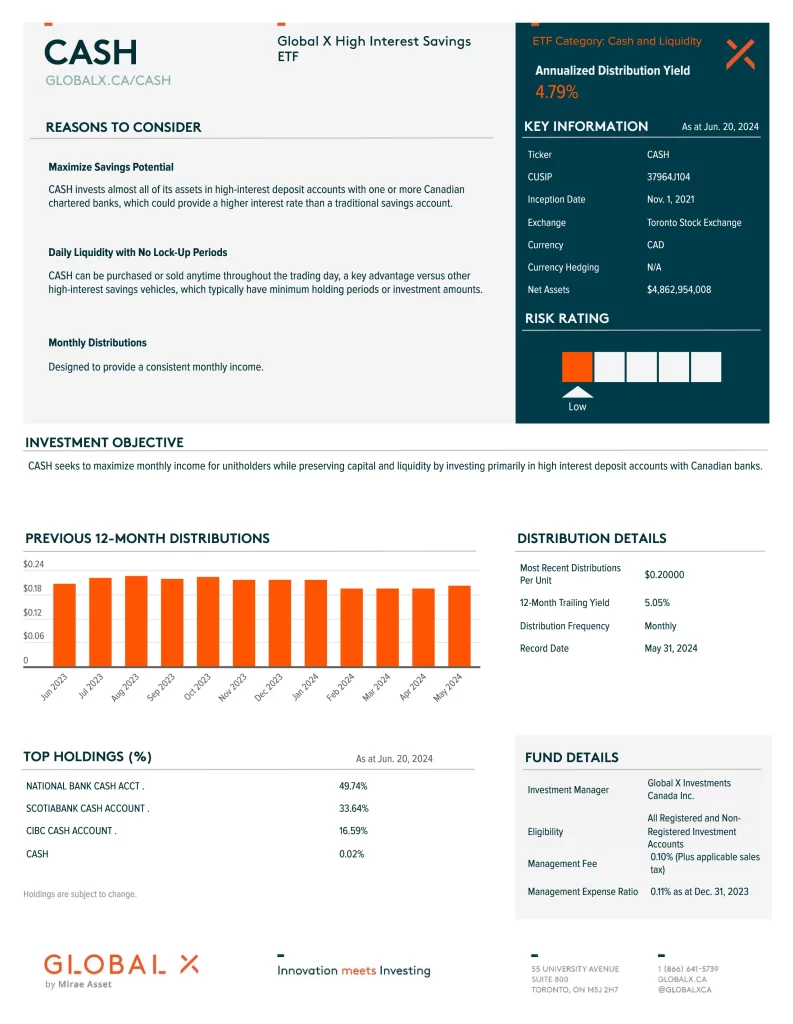
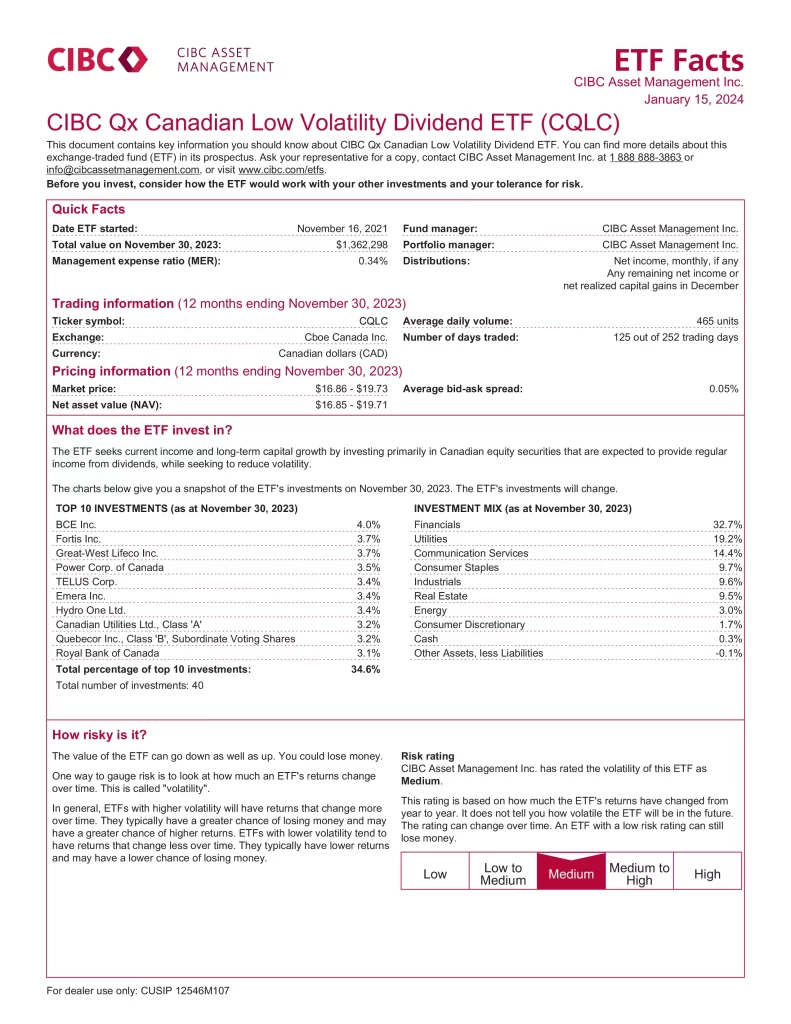
Investing 101 is perfect for anyone wanting to grasp the basics of investing. Learn how the stock market works, explore different types of investments, understand the risks, and get the tools to get started. What you’ll learn:
- Key investing concepts like risk, time horizon, and how the stock market functions.
- How to manage risk through diversification and assess your personal risk tolerance.
- How to set your investing goals and decide the best way to hold your investments.
- How to verify the registration of your investment advisor and recognize signs of fraud.
Saving Versus Investing
Saving and investing are both important, but there are differences in how they can help you plan for the future. There are many investment options available. To get started, here are a few questions to ask:
- How much do you have to save each month to reach your goals?
- Will you need to change your spending habits to save money or pay off debt?
- Would you be able to pay your bills if you lost your job or had an accident and couldn’t work?
- What are the tax implications for your investments?
- What professional support would help you to reach your goals? (i.e. debt professional, financial advisor, investment broker, etc.)
What is an ETF?
Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) are investment funds, providing investors access to a basket of securities that trade on an exchange like a stock. They deliver a combination of benefits shared by stocks and/or mutual funds.
What is an Equity?
Equity represents a fractional ownership stake in a company, denominated in “shares” and traded on a stock exchange. If the company is successful, shareholders tend to benefit; if the company fails, shareholders may lose their investment as assets are distributed to bondholders.
What is Fixed Income?
Fixed income generally refers to debt borrowed by a company or government. Bond buyers, in effect, lending money to the issuer, which agrees to pay a pre-set interest rate, as well as return the amount invested on the maturity date.
What is a GIC?
A Guaranteed Investment Certificate (GIC) is an investment that protects your invested capital over a pre-determined period of time. They can have either a fixed or a variable interest rate and are available in various maturities.
What is a Mutual Fund?
Mutual funds are professionally managed investments, providing investors access to a portfolio of assets (for example, bonds, stocks) that many people wouldn’t be able to afford by themselves.
What is a Segregated Fund?
Similar to a mutual fund, a segregated fund is issued by an insurance company. Its primary distinction is that upon maturity, regardless of investment returns, the investor is guaranteed to receive at least a pre-set minimum percentage of their payments into the fund.
Alternative Investments
There are two broad “alternative” categories. The first invests in non-traditional assets with returns that tend not to be correlated to stocks or bonds. These include commodities (oil, gold, etc.), infrastructure (ports, highways, etc.), and real estate. The second type of alternative uses non-traditional strategies, like short-selling
Important Investing Terms
- Beta: A measure of the volatility, or systematic risk, of a security or a portfolio in comparison to the market as a whole
- Correlation: A statistical measure of how two securities move in relation to one another
- Positive correlation indicates similar movements, up or down, while negative correlation indicates opposite movements (when one rises, the other falls
- Credit Rating/Risk: An assessment of the creditworthiness of a borrower in general terms or with respect to a particular debt or financial obligation
- Credit risk is the risk of default on a debt that may arise from a borrower failing to make required payment.
- Duration: A measure of the sensitivity of the price of a fixed income investment to a change in interest rates
- Duration is expressed as number of years
- The price of a bond with a longer duration would be expected to rise (fall) more than the price of a bond with lower duration when interest rates fall (rise)
- Interest Rate Risk: Refers to the chance that investments in bonds will suffer, as the result of unexpected interest rate changes
- Leverage: An investment strategy of using borrowed money to increase the potential return of an investment
- Liquidity: The degree to which an asset or security can be quickly bought or sold in the market without affecting the asset’s price
- Cash is considered to be the most liquid asset, while things like fine art or rare books would be relatively illiquid
- Risk: Often considered the potential of losing your money when investing; it can also refer to the level of volatility of an investment
- Generally speaking, the higher the risk, the higher the return potential
- Standard Deviation: A measure of risk in terms of the volatility of returns
- It represents the historical level of volatility in returns over set periods
- A lower standard deviation means the returns have historically been less volatile and vice-versa
- Historical volatility may not be indicative of future volatility
- Volatility: Measures how much the price of a security, derivative, or index fluctuates
- The most commonly used measure of volatility when it comes to investment funds is standard deviation
What is Important for You?
- Rate of Return
- Service
- Proximity of the Branch
- Retirement Plan
- Withdrawn Strategy
- Tax Efficiency
Financial Advisor & Investment Fees
The costs associated with having professionals manage your money vary, but generally fall into these categories:
- Investment Management Fee
- Operating Expenses
- Sales Tax
- Financial Planning & Advice
Emergency Fund
Have you put some funds aside for emergencies? An emergency fund is a set amount of money kept aside to cover unexpected expenses. It can help you avoid debt by providing a financial safety net to cover essential living expenses.
- Car repairs
- Job loss
- Veterinarian visit
- Health problems
- Natural disaster
Asset Classes
The importance of diversification is no great secret. Asset classes do not always move in tandem; stock prices may be up when bond prices are down and vice versa.
- Alternatives: Sustainable investing or responsible investing refers to investment strategies that aim to create long-term value for investors while also contributing to a better environment, healthier communities and good corporate governance practices
- Balanced: A balanced fund holds both equity and fixed income securities
- These funds can be split between stocks and bonds depending on preference
- This strategy aims to seek a balance between growth and preserving capital
- Equities: Equities (also known as shares or stocks) represent ownership in a company
- By owning a stake in a company, your investments can grow if the company does well – or shrink if the company struggles.
- Fixed Income: A fixed income security is one where the issuer must make payments on a schedule, the most common type being a bond
- This investment type may stabilize overall portfolio volatility, preserve capital control risk and generate income
- Sustainable Investing: Sustainable investing or responsible investing refers to investment strategies that aim to create long-term value for investors while also contributing to a better environment, healthier communities and good corporate governance practices
Dollar Cost Averaging (DCA)
The power of dollar cost averaging (DCA) involves buying equal dollar amounts of a given investment on a regular basis. Rather than investing all your money at once, making a commitment to invest a smaller amount on a regular basis may lower your average cost per unit by purchasing more units at lower prices.
Conclusion
ETFs have become a popular investment option that provides an easy-to-use, low-cost way to invest. They offer diversified exposure and contain a portfolio of securities designed to track a specific index or market sector, or produce a specific outcome.
- What type of financial investment is it?
- A mutual fund or an ETF?
- What fees might be charged?
- How is it managed?
- Is it environmentally friendly?
- How are the investments taxed?
- What are your expectations regarding the rate of return on your investments and are you achieving that goal?
- Why have you decided to do business with other financial institutions?