Although we can’t control the markets, we can control our response to them. Market volatility can feel unsettling, especially when the future of our investments seems uncertain and beyond our control. After a long spell of positive returns, it can come as a tremendous shock to be reminded that volatility includes stock prices going down as well as up. The truth is, such movement is practically guaranteed. While you can’t control the markets, you can manage how you react to their swings.
What is Volatility?
Volatility refers to the degree of price fluctuations for an asset, whether an individual stock, an entire market, or a portfolio. Fluctuating prices aren’t unique to stock markets. The amount a price changes indicates its volatility. High volatility, especially during market corrections, can feel unsettling. Frequent, short-term declines can spark fears of a larger market downturn.
What Can You Do During Stock Market Volatility?
It’s important to remember that no one can predict exactly when the markets will rise or fall or precisely how significant that change will be. However, we can control how we react to those market events. Predicting the direction the economy will take and how financial markets will evolve is difficult, requiring the integration of many variables and highly sophisticated valuation models.
Control Your Emotions
Learning to control your emotions will help you reach your goals. It’s normal to be nervous when markets are volatile. But left unchecked, emotions can lead to bad decisions. The curve below represents stock market fluctuations. It shows how most investors react as the market and the value of their growth stocks fluctuate.
Stay Invested
There are better days ahead. The biggest gains often follow market corrections. Pulling your money out early can hurt the long-term performance of your investments. Don’t miss the potential of the best days!
Invest Regularly
Capitalize on market opportunities. No one can predict the market. That’s why it’s best to invest regularly. Take advantage of market downturns and don’t just buy when prices are high. With dollar cost averaging, you’ll have the best chance of getting the best average cost per share and capitalizing on market opportunities.
Diversify Your Portfolio
Past performance is no guarantee. It’s important to diversify your investments. A portfolio with a variety of industries, management styles, countries and asset classes will have a higher return potential and be less vulnerable to volatility.
Stay on Track
In periods of high volatility, you may be tempted to deviate from your long-term investment strategy by “parking” your money in so-called safer investments. However, the cost of this short-term solution can be very high if you miss out on a significant rebound.
Work with a Professional
Seek the help of a professional. Talk to a professional for expert, objective advice tailored to your financial situation. Studies have shown that people who work with an advisor tend to be in better financial health.
How to Manage During Stock Market Volatility
Remember, no one can predict exactly when markets will rise or fall or the extent of those changes. However, we can control how we respond to market fluctuations. Here are three tips to help you stay grounded during periods of volatility:
- Don’t Focus on Today’s Price if You Don’t Need the Money Now: If you’re not planning to use your invested money right away, today’s market price isn’t as relevant. Consider the housing market as an example: if prices drop but you’re not selling your home anytime soon, the temporary decline doesn’t impact you directly. Likewise, with investments, if you’re focused on long-term goals, you can stay patient through market ups and downs.
- Avoid Trying to Time the Market: Timing the market is extremely challenging and often counterproductive. For instance, missing just the 10 best days over the past 20 years could have halved your return, and missing the top 30 days would have turned your gain into a loss. Holding steady is often a better strategy than attempting to guess market highs and lows.
- Less Volatile or Defensive Stocks: These companies have outperformed the broad market over the long-term, as less volatile stocks may benefit from a smaller decline during market corrections while still increasing during advancing markets. Additionally, low volatility stocks tend to be more mature and have a higher dividend yield than the broad market. The higher dividend yield helps to minimize swings in portfolio value.
Focus on Beta
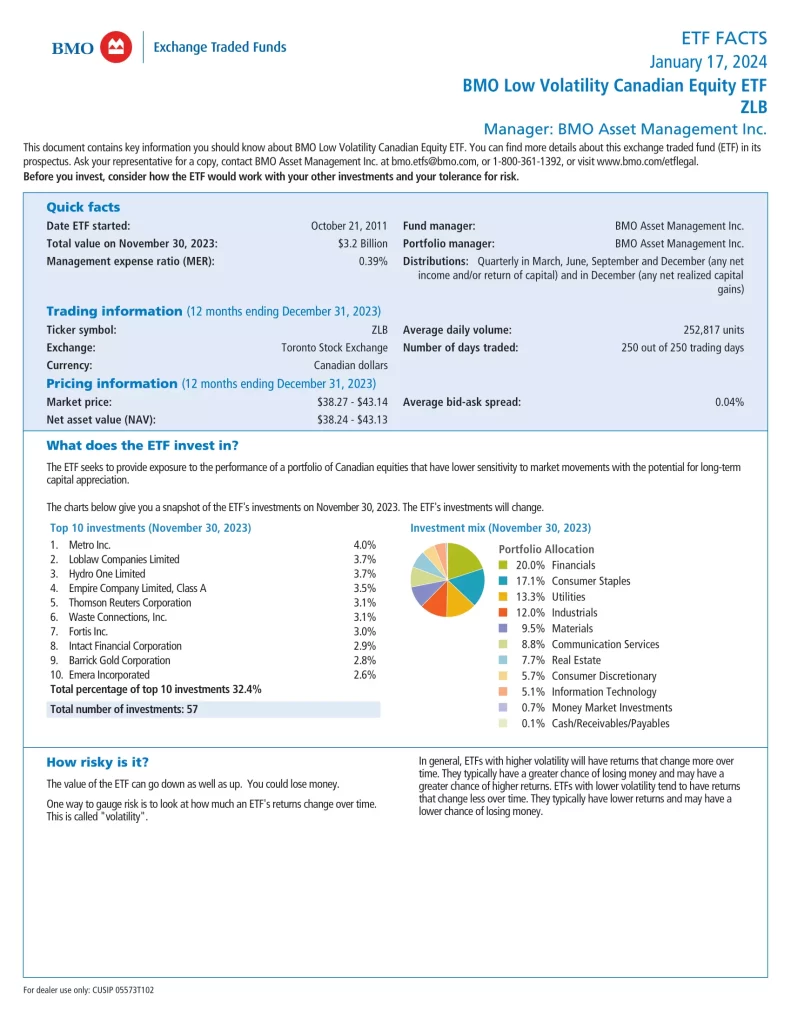
To develop our low volatility strategy, we identified beta as the most appropriate risk metric as it measures a security’s sensitivity to the movements of the broad market. The broad market has a beta value of 1. A beta less than 1 indicates a security is less risky relative to the broad market. By selecting securities with lower betas, investors are able to access a portfolio that is designed to reduce market risk.
Beta is a smarter portfolio construction tool when compared to standard deviation (stock’s volatility relative to itself) because it does a better job at sheltering investors from large market events.
Watching from the Sidelines May Cost You
When markets become volatile, many try to guess when stocks will bottom out. In the meantime, they often park their cash investments. But just as many investors are slow to recognize a retreating stock market, many also fail to see an upward trend until after they have missed opportunities for gains. Missing out on these opportunities can take a big bite out of your returns.
Conclusion
Staying calm and focused on your long-term goals can help you navigate market volatility more confidently. Focus on the factors of your you can control, including things such as asset allocation and costs, and not worry about investing strategy about those things out of your control, such as downturns in the markets and economy. In the meantime, remember that bearish market conditions, while inevitable, don’t last forever. Downturns come and go.